Bitcoin Without Borders: Unlocking Bitcoin's Multi-Chain Potential
Since the birthday of the first Bitcoin block on January 3, 2009, a new era of financial assets has begun - the cryptocurrency era. Unmatched security, permissionlessness, and decentralization cemented Bitcoin's place at the very top of this new asset class and the most domineering force on the
•
5 min read

Since the birthday of the first Bitcoin block on January 3, 2009, a new era of financial assets has begun - the cryptocurrency era. Unmatched security, permissionlessness, and decentralization cemented Bitcoin's place at the very top of this new asset class and the most domineering force on the market. However, every titan has a weakness, and for Bitcoin, it's limited programmability. This drawback stifled its expansion into new financial markets.
In the summer of 2020, a new wave of cryptocurrency adoption called DeFi (Decentralized Finance) brought crypto users lots of financial products like trading, lending, borrowing, derivatives, and many more. Ethereum brought more functionality to cryptocurrency, filling the gap that Bitcoin couldn't at the time. More than five years have passed, and the most secure flagman crypto asset - Bitcoin - is still rarely used in DeFi, keeping $1.6T as of April 2025 of Bitcoin liquidity disjointed from DeFi markets. The apparent reason is the lack of a solution that connects Bitcoin to the DeFi ecosystem, which meets Bitcoin users' security requirements, who historically value security the most.
BTC <> DeFi risks
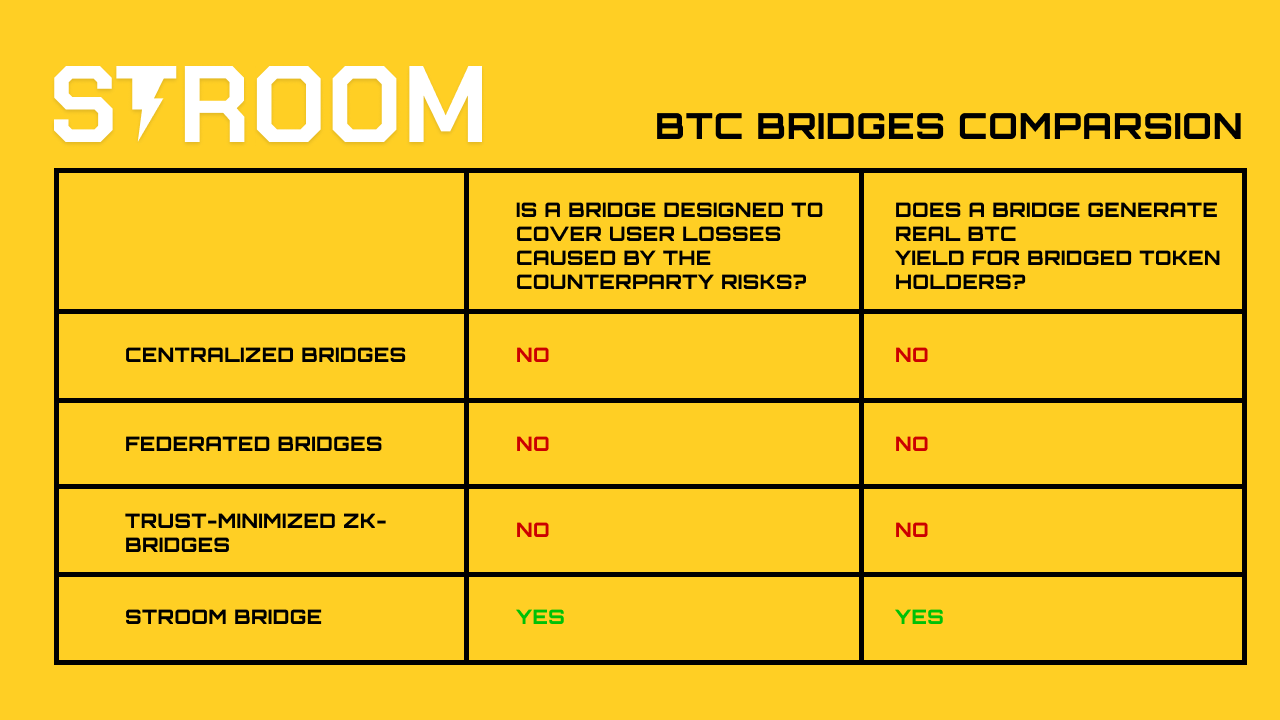
Well, what are my options if I have BTC and want to utilize it in DeFi? Frankly, there is only one option - use a Bitcoin bridge. A Bitcoin bridge is a connector that allows data to be transferred from the Bitcoin blockchain to another, such as Ethereum. During this transfer, the original Bitcoins are locked on a Bitcoin script, and a tokenized version of Bitcoin is created on the destination chain (a chain where Bitcoins are bridged), commonly called wrapped Bitcoin. Yet, bridging an asset bears two main caveats.
The first one is security. Whether it's a bridge or an alternative, protocol or smart-contact exploits could lead to losing a portion or, in the worst-case scenarios, to a complete loss of users' funds. Also, collusion or malicious intent is possible when a centralized entity or a group of representatives operates the bridging process, leading to the same result as in an exploit.
Currently, there is no genuinely decentralized permissionless BTC bridge. However, BitVM2's architecture with SNARK proof verification script and Stroom's economic security with restaking provide sufficient technology to minimize those risks.
The second threat is connected with economic benefits. While moving BTC to other chains can lead to increased usability in DeFi, the associated deposit/withdrawal fees can nullify the anticipated returns. Stroom solves this by offering its users low-risk yields on the deposited BTC. By generating additional APY on BTC instead of keeping them inactive, Stroom not only enlarges the upside for BTC bridging but actively stimulates the Bitcoin ecosystem in general, which leads to a higher appreciation of BTC as a financial asset.
Now that the risks are laid out, let's examine bridge types and potential workarounds in detail.
Centralized bridges are platforms or services that facilitate the transfer of Bitcoin between different blockchains or networks, with a centralized authority controlling the process. These bridges typically involve users sending their Bitcoin to a trusted custodian, who then issues an equivalent amount of wrapped or tokenized Bitcoin on another blockchain, such as Ethereum or Solana. While centralized bridges offer faster and simpler cross-chain transfers, they rely on a central entity to manage funds and operations, which introduces potential risks such as counterparty risk, security breaches, and a lack of decentralization.
Federated bridges are decentralized mechanisms that allow Bitcoin to be transferred across different blockchains, leveraging a group of trusted entities, or "federated nodes," to manage the process. In these systems, a federation of participants (usually multiple organizations or individuals) collectively oversees the locking and unlocking of Bitcoin on the Bitcoin blockchain and the minting of tokenized Bitcoin on another blockchain. Federated bridges distribute control and responsibility across multiple participants, reducing single points of failure and enhancing security. However, they still require trust in the federation.
Trust-minimized zk-bridges are decentralized communication protocols that leverage zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) to minimize reliance on trusted intermediaries. They work under the assumption that as long as at least one intermediary stays honest, the bridge integrity is intact. The BitVM2 paradigm is the basis for novel technological solutions in this niche. Nevertheless, in the BitVM2 setup, native BTC remains locked in a complex script, making it impossible to use this liquidity in yield-generating opportunities.
Stroom bridge isn't yet a dedicated type of bridge but rather a unique construct, addressing two major bridging problems: counterparty concerns and opportunity cost. When users bridge their BTC, they face a complicated question: "How can I keep the minimum level of risk and earn on the BTC holdings?"
Stroom proposes a distinctive solution - an economically secured yield-bearing BTC. Economic security is provided by a federated multi-collateral bridge built on restaking while locked BTC liquidity on the Bitcoin blockchain instead of remaining idle on a multi-sig wallet is being utilized for real yield generation starting from Lightning Network, then adding BitVM bridge operations, Core DAO, and Babylon staking, etc.
Earned yield is distributed between Stroom users and bridge operators, paying for keeping the economic security.
Bitcoin bridging alternatives
It is worth noting that, from a technical perspective, the options mentioned below cannot be considered a bridging alternative until someone else has created a tokenized version of BTC on a destination chain like Ethereum. Nonetheless, from a user perspective, we can consider them as bridging alternatives.
Atomic swaps are peer-to-peer exchanges of crypto assets across different blockchains. They operate with Hash Timelock Contracts (HTLCs), ensuring both parties fulfill their part of a trade in a defined time or the trade doesn't happen at all. To perform an atomic swap, both BTC on the native chain and a wrapped BTC on the bridging chain should already be created.
Cross-chain Decentralized exchange (DEX) is a platform that employs a liquidity pool model, where users provide liquidity by depositing their assets into smart contracts. Swapping BTC to another asset when using DEX, users lose price exposure. To be deemed a cross-chain DEX, it must operate on two or more blockchains. As with atomic swaps, DEX can't substitute for bridging without a preexisting liquidity pool with a wrapped BTC.
Layer 2 blockchains are complementary networks to existing blockchains, Layer 1s, and are built on top of them. Usually, Layer 2 solutions address the scalability challenges their corresponding Layer 1s face. The most prominent Layer 2 on Bitcoin is the Lightning Network.
Conclusion
The Bitcoin DeFi ecosystem, or BTCFi, is only at the dawn of its development. The variety and quantity of applications on other chains are far greater than on Bitcoin.
Still, as the most dominant and secure asset, Bitcoin should eventually overcome the lack of exposure to decentralized finances, and cutting-edge technologies like Stroom or BitVM2 only spur excessive dormant BTC liquidity to be actively used.
To learn more about Stroom, access detailed information about our technology, or explore how you can join the ecosystem, visit the following resources:
Official website: https://stroom.network/
Whitepaper: https://stroom.network/Primer.pdf
Twitter (X): https://twitter.com/StroomNetwork
Discord: https://discord.gg/DZ53WjDXz9
Telegram: https://t.me/stroomnetwork

Stroom DAO
View our other posts

Lightning Network in 2025: Bitcoin’s Transformation into Everyday Money
Bitcoin’s Lightning Network is transforming from an experiment into a global payment system, making everyday transactions faster and cheaper.
Stroom DAO

Lightning Network: Celebrating 9 Years of Innovation
The Lightning Network whitepaper was unveiled on January 14, 2016, introducing a transformative layer atop Bitcoin for instant, scalable transactions.
Stroom DAO

Mapping Lightning Network - Scaling Bitcoin for Global Payments
Explore a detailed map of the Lightning Network ecosystem—key tools, wallets, and innovations driving faster, cheaper, and scalable Bitcoin payments worldwide.
Stroom DAO